Abstract
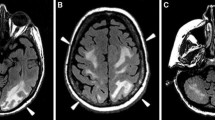
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome is a well-recognized entity associated with a variety of benign and malignant conditions. This syndrome typically manifests itself with headache, visual loss, and seizures. Radiographic abnormalities consist of white matter edema involving the posterior parietal and occipital lobes, manifested as increased T2 and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging. In the last decade, there has been a reported increase in the incidence of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in cancer patients. The diagnosis can be challenging in this patient population. Early recognition and initiation of appropriate therapy with removal of the causative agent is essential in order to prevent permanent neurologic sequelae.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(8):494–500.
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF. Distinct imaging patterns and lesion distribution in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(7):1320–7.
Bartynski WS. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 2: controversies surrounding pathophysiology of vasogenic edema. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(6):1043–9.
Lamy C, Oppenheim C, Meder JF, Mas JL. Neuroimaging in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Neuroimaging. 2004;14(2):89–96.
Yasuhara T, Tokunaga K, Hishikawa T, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18:406–9.
Li Y, Gor D, Walicki D, et al. Spectrum and potential pathogenesis of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. J Stroke CerebrovascDis. 2012;21(8):873–82. This is a retrospective single-center case series which identifies clinical and neuroimaging features, as well as various pathophysiologic causes of PRES.
Tsukamoto S, Takeuchi M, Kawajiri C, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in an adult patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after remission induction chemotherapy. Int J Hematol. 2012;95:204–8.
Bhatt A, Farooq MU, Majid A, Kassab M. Chemotherapy-related posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2009;5(3):163–9.
Ni J, Zhou LX, Hao HL, et al. The clinical and radiological spectrum of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a retrospective series of 24 patients. J Neuroimaging. 2011;21:219–24. This is a retrospective single-center case series which identifies clinical and neuroimaging features of PRES.
Iwama M, Takahashi H, Takagi R, Hiraoka M. Permanent bilateral cortical blindness due to reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. J Nippon Med Sch. 2011;78:184–8.
Liman TG, Bohner G, Heuschmann PU, et al. The clinical and radiological spectrum of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: the retrospective Berlin PRES study. J Neurol. 2012;259:155–64. This is a retrospective multicenter case series which identifies clinical and neuroimaging features of PRES.
Mueller-Mang C, Mang T, Pirker A, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: do predisposing risk factors make a difference in MRI appearance? Neuroradiology. 2009;51:373–83.
Munoz J, Kumar V, Hamilton J, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: more than meets the eye. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(20):360–3.
Hart C, Kinney MO, McCarron MO. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and oral methotrexate. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012;114:725–7.
Fugate JE, Claasseen DO, Cloft HJ. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: associated clinical and radiologic findings. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85(5):427–32.
Hugonnet E, Da Ines D, Boby H, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): features on CT and MR imaging. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94:45–52. This is a review article which identifies various neuroimaging features in different clinical settings.
Roth C, Ferbert A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: long term follow-up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010;81:773–7.
Burrus TM, Mandrekar J, Wijdicks EM, et al. Renal failure and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Arch Neurol. 2010;67(7):831–4.
Patejdl R, Borchert K, Pagumbke H, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): an unusual primary manifestation of a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2011;113:819–21.
Stubgen JP. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) after granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) therapy. J Neurol Sci. 2012;321:35–8.
Seet RCS, Rabinstein AA. Clinical features and outcomes of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome following bevacizumab treatment. Q J Med. 2012;105:69–75.
Chen YH, Huang CH. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome induced by vinorelbine. Clin Breast Cancer. 2012;12(3):222–5.
Aradillas E, Arora R, Gasperino J. Methotrexate-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2011;36:529–36.
Stott VL, Hurrell MA, Anderson TJ. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a misnomer reviewed. Intern Med J. 2005;35(2):83–90.
Rajasekhar A, George Jr TJ. Gemcitabine-induced reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Oncologist. 2007;12(11):1332–5.
Abali H, Eren OO, Dizdar O, et al. Posterior leukoencephalopathy after combination chemotherapy in a patient with lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46(12):1825–8.
Vieillot S, Pouessel D, de Champfleur NM, Becht C, Culine S. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome after carboplatin therapy. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(3):608–9.
Moris G, Ribacoba R, Gonzalez C. Delayed posterior encephalopathy syndrome following chemotherapy with oxaliplatin and gemcitabine. J Neurol. 2007;254(4):534–5.
Koopman M, Muller EW, Punt CJ. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome caused by bevacizumab: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008;51(9):1425–6.
Kwon EJ, Kim SW, Kim KK, Seo HS, Kim do Y. A case of gemcitabine and Cisplatin associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Cancer Res Treat. 2009;41(1):53–5.
Pinedo DM, Shah-Khan F, Shah PC. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome associated with oxaliplatin. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(33):5320–1.
Govindarajan R, Adusumilli J, Baxter DL, El-Khoueiry A, Harik SI. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome induced by RAF kinase inhibitor BAY 43-9006. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(28):e48.
Connolly RM, Doherty CP, Beddy P, O'Byrne K. Chemotherapy induced reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Lung Cancer. 2007;56(3):459–63.
Haefner MD, Siciliano RD, Widmer LA, Vogel Wigger BM, Frick S. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome after treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Onkologie. 2007;30(3):138–40.
Vaughan CJ, Delanty N. Hypertensive emergencies. Lancet. 2000;356(9227):411–7.
Adams Jr HP, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, et al. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research interdisciplinary working groups: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Circulation. 2007;115(20):e478–534.
Kwon S, Koo J, Lee S. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Pediatr Neurol. 2001;24(5):361–4.
Hammerstrom AE, Howell J, Gulbis A, et al. Tacrolimus-associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in hematopoietic allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2013;88:301–5.
Sharief U, Perry DJ. Delayed reversible posterior encephalopathy syndrome following chemotherapy with oxaliplatin. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2009;8(3):163–5.
Ozcan C, Wong SJ, Hari P. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome and bevacizumab. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(9):980–2. discussion 980-2.
Wong R, Beguelin GZ, de Lima M, et al. Tacrolimus-associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol. 2003;122(1):128–34.
Zeigler ZR, Shadduck RK, Nemunaitis J, Andrews DF, Rosenfeld CS. Bone marrow transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a case series. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15(2):247–53.
Shah-Khan F, Pinedo D, Shah P. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome and anti-neoplastic agents: a review. Oncol Rev. 2007;1(3):152–61.
Vaughn C, Zhang L, Schiff D. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2008;10(1):86–91.
Strandgaard S, Paulson OB. Cerebrovascular consequences of hypertension. Lancet. 1994;344(8921):519–21.
Sanders AB. Hypertensive emergencies. Am Fam Physician. 1991;44(5):1767–74.
Marinella MA, Markert RJ. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome associated with anticancer drugs. Intern Med J. 2008;39:826–34.
Lee VH, Wijdicks EF, Manno EM, Rabinstein AA. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2008;65(2):205–10.
Nuver J, Smit AJ, van der Meer J, et al. Acute chemotherapy-induced cardiovascular changes in patients with testicular cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(36):9130–7.
Cossaart N, SantaCruz KS, Preston D, Johnson P, Skikne BS. Fatal chemotherapy-induced encephalopathy following high-dose therapy for metastatic breast cancer: a case report and review of the literature. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003;31(1):57–60.
Kane RC, Farrell AT, Saber H, et al. Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(24):7271–8.
Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Bukowski RM, et al. Sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. JAMA. 2006;295(21):2516–24.
Tam CS, Galanos J, Seymour JF, Pitman AG, Stark RJ, Prince HM. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome complicating cytotoxic chemotherapy for hematologic malignancies. Am J Hematol. 2004;77(1):72–6.
Allen JA, Adlakha A, Bergethon PR. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome after bevacizumab/FOLFIRI regimen for metastatic colon cancer. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(10):1475–8.
Pruitt A, Graus F, Rosenfeld M. Neurological complications of transplantation: part I: hematopoietic cell transplantation. Neurohospitalist. 2013;3(1):24–38.
Reece DE, Frei-Lahr DA, Shepherd JD, et al. Neurologic complications in allogeneic bone marrow transplant patients receiving cyclosporin. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1991;8(5):393–401.
Bartynski WS, Zeigler ZR, Shadduck RK, Lister J. Pretransplantation conditioning influence on the occurrence of cyclosporine or FK-506 neurotoxicity in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25(2):261–9.
Zimmer WE, Hourihane JM, Wang HZ, Schriber JR. The effect of human leukocyte antigen disparity on cyclosporine neurotoxicity after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19(4):601–8. discussion 609-10.
Furukawa M, Terae S, Chu BC, Kaneko K, Kamada H, Miyasaka K. MRI in seven cases of tacrolimus (FK-506) encephalopathy: utility of FLAIR and diffusion-weighted imaging. Neuroradiology. 2001;43(8):615–21.
Siddiqui TS, Haq IU, Rehman B, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012;22(3):168–70.
Naqi R, Azeemuddin M. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Pak Med Assoc. 2012;62(7):657–60.
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF, Zeigler ZR, Shadduck RK, Lister J. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in infection, sepsis, and shock. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(10):2179–90.
Gijtenbeek JM, van den Bent MJ, Vecht CJ. Cyclosporine neurotoxicity: a review. J Neurol. 1999;246(5):339–46.
Casey SO, Sampaio RC, Michel E, Truwit CL. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: utility of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in the detection of cortical and subcortical lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21(7):1199–206.
Garg RK. Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 2001;77(903):24–8.
Lunardi N, Saraceni E, Boccagni P. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in the intensive care unit after liver transplant: A comparison of our experience with the existing literature. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012;78(7):847–50.
Di Nisio M, Soesan M, Otten HM. Endothelial damage of the internal carotid artery after chemoradiotherapy of the neck for a Hodgkin lymphoma. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97(2):315–6.
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23(6):1038–48.
Sibai BM. Medical disorders in pregnancy, including hypertensive diseases. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 1990;2(1):13–22.
Ito T, Sakai T, Inagawa S, Utsu M, Bun T. MR angiography of cerebral vasospasm in preeclampsia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995;16(6):1344–6.
Bakshi R, Bates VE, Mechtler LL, Kinkel PR, Kinkel WR. Occipital lobe seizures as the major clinical manifestation of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: magnetic resonance imaging findings. Epilepsia. 1998;39(3):295–9.
Demirel I, Ozer AB, Bayar MK, et al. Anesthesia and intensive care management in a pregnant woman with PRES: a case report. Case Rep Anesthesiol. 2012. doi:10.1155/2012/745939.
Erdogan FF, Ozkan S. A rare entity in ED: Posterior reversible encephalopathy. Am J Emerg Med. 2099;2012(30):e1–3.
Andrews P, Azoulay E, Antonelli M, et al. Year in review in intensive care medicine, 2005. II. Infection and sepsis, ventilator-associated pneumonia, ethics, haematology and haemostasis, ICU organisation and scoring, brain injury. Intensive Care Med. 2006;32(3):380–90.
Andrews P, Azoulay E, Antonelli M, et al. Year in review in intensive care medicine, 2004. III. Outcome, ICU organisation, scoring, quality of life, ethics, psychological problems and communication in the ICU, immunity and hemodynamics during sepsis, pediatric and neonatal critical care, experimental studies. Intensive Care Med. 2005;31(3):356–72.
Striano P, Striano S, Totora F, et al. Clinical spectrum and critical care management of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). Med Sci Monit. 2005;11(11):549–53.
Finsterer J, Schlager T, Kopsa W, Wild E. Nitroglycerin-aggravated pre-eclamptic posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). Neurology. 2003;61(5):715–6.
Harkany T, Dijkstra IM, Oosterink BJ, et al. Increased amyloid precursor protein expression and serotonergic sprouting following excitotoxic lesion of the rat magnocellular nucleus basalis: neuroprotection by Ca2+ antagonist nimodipine. Neuroscience. 2000;101(1):101–14.
Rosetti AO, Lowenstein DH. Management of refractory status epilepticus in adults: still more questions than answers. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:922–30.
Kozak OS, Wijdicks EF, Manno EM, Miley JT, Rabinstein AA. Status epilepticus as initial manifestation of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Neurology. 2007;69(9):894–7.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Eileen M. Le and Monica E. Loghin declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Neuro-oncology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, E.M., Loghin, M.E. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: A Neurologic Phenomenon in Cancer Patients. Curr Oncol Rep 16, 383 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-014-0383-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-014-0383-3