Abstract
Purpose
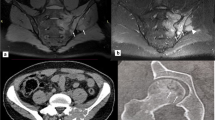
The authors retrospectively reviewed six cases of histologically proven Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD) to evaluate organ involvement and clinical and radiological findings.
Materials and methods
Through a search of the pathology databases of four Italian hospitals, we identified six men (mean age, 56 years) with a histological diagnosis of ECD. Histology was performed on retroperitoneal or pulmonary biopsy, depending on disease involvement on imaging. Patients underwent plain radiography of the lower limbs and chest, total-body computed tomography (CT) and bone scintigraphy. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging was performed in two patients to evaluate the lower limbs and in one patient to study the brain, the chest and the abdomen.
Results
Clinical manifestations included dyspnoea (n=2), hydronephrosis (n=2) and bone pain (n=1). Bilateral symmetrical osteosclerosis of the metaphyseal and diaphyseal portions of the lower-limb long bones was present in five patients. Imaging studies revealed extraskeletal manifestations in all patients, including involvement of the retroperitoneal space (n=4), the lung (n=4) and the heart (n=2).
Conclusions
ECD is a multiorgan disease that displays constant involvement of the bones and retroperitoneum; in particular, of the perirenal fat. Although the diagnosis of ECD is histological, imaging can raise suspicion and help to establish a presumptive diagnosis.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Valutare retrospettivamente la prevalenza dell’impegno nei differenti organi e gli aspetti clinico-radiologici in 6 pazienti con diagnosi istologica di malattia di Erdheim-Chester.
Materiali e metodi
Sono stati identificati nel data base dell’unità operativa di anatomia patologica di quattro ospedali italiani, sei pazienti con ECD, di sesso maschile, con età media di 56 anni. L’esame istologico era stato effettuato mediante biopsie retroperitoneali o polmonari, a seconda dell’impegno della patologia, valutato sull’imaging radiologico. I pazienti erano stati sottoposti a: indagine radiografica standard degli arti inferiori e del torace, tomografia computerizzata toracica e addominale e scintigrafia ossea. In due pazienti è stata eseguita risonanza magnetica (RM) per una valutazione degli arti inferiori. Un paziente fu sottoposto ad RM dell’encefalo, del torace e dell’addome.
Risultati
Le manifestazioni cliniche comprendevano: dispnea (2 pazienti), idronefrosi (2 pazienti) e dolore osseo (1 paziente). L’osteosclerosi bilaterale simmetrica delle metafisi e delle diafisi degli arti inferiori era presente nella maggior parte dei pazienti (5). Gli esami radiologici documentavano localizzazioni extraossee in tutti i pazienti: retroperitoneale (4 pazienti), polmonare (4 pazienti) e cardiaco (2 pazienti).
Conclusioni
L’ECD è una malattia multiorgano che coinvolge sempre, nella nostra esperienza, il tessuto scheletrico ed il retroperitoneo, in particolare gli spazi perirenali. La diagnosi di natura dell’ECD è istologica, tuttavia il sospetto diagnostico può essere agevolmente posto con l’imaging radiologico.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Chester W (1930) Über lipoidgranulomatose. Virchows Arch (Path Anat) 279:561–602
Resnick D, Greenway G, Genant H et al (1982) Erdheim-Chester disease. Radiology 142:289–295
Kenn W, Eck M, Allolio B et al (2000) Erdheim-Chester disease: evidence for a disease entity different from Langerhans cell histiocytosis? Three cases with detailed radiological and immunohistochemical analysis. Hum Pathol 31:734–739
Bancroft LW, Berquist TH (1998) Erdheim-Chester disease: radiographic findings in five patients. Skeletal Radiol 27:127–132
Breuil V, Brocq O, Pellegrino C et al (2002) Erdheim-Chester disease: typical radiological bone features for a rare xanthogranulomatosis. Ann Rheum Dis 61:199–200
Gomez C, Diard F, Chateil JF et al (1996) Imaging of Erdheim-Chester disease. J Radiol 77:1213–1221
Dion E, Graef C, Miquel A et al (2006) Bone involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: imaging findings including periostitis and partial epiphyseal involvement. Musculoskeletal Imaging 238:632–639
Jaffe HL (1972) Lipid cholesterol granulomatosis. In: Lea F (ed) Metabolic, degenerative and inflammatory diseases of bone and joints. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 535–541
Veyssier-Belot C, Cacoub P, Caparros-Lefebvre D et al (1996) Erdheim-Chester disease: clinical and radiologic characteristics of 59 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 75:157–169
Chetritt J, Paradis V, Dargere D et al (1999) Erdheim-Chester disease: a neoplastic disorder. Hum Pathol 30:1093–1096
Al-Quran S, Reith J, Bradley J et al (2002) Erdheim-Chester disease: case report, PCR-based analysis of clonality, and review of literature. Mod Pathol 15:666–672
Vencio EF, Jenkins RB, Schillet JL et al (2007) Clonal cytogenetic abnormalities in Erdheim-Chester disease. Am J Surg Pathol 31:319–321
Greenberger JS, Crocker AC, Vawter G et al (1981) Results of treatment of 127 patients with systemic histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe syndrome, Schuller-Christian syndrome and multifocal eosinophilic granuloma). Medicine (Baltimore) 60:311–338
Murray D, Marshall M, England E et al (2001) Erdheim-Chester disease. Clin Radiol 56:481–484
Kushihashi T, Munechika H, Sekimizu M et al (2000) Erdheim-Chester disease involving bilateral lower extremities: MR features AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:875–876
Yamamoto T, Mizuno K (2000) Erdheim-Chester disease with intramuscular lipogranuloma. Skeletal Radiol 29:227–230
Kim NR, Ko YH, Choe YH et al (2001) Erdheim-Chester disease with extensive marrow necrosis: a case report and literature review Int J Surg Pathol 9:73–79
Sandrock D, Merino M, Scheffknecht B et al (1990) Scintigraphic findings and follow up in Erdheim-Chester disease. Eur J Nucl Med 16:55–60
Ivan D, Neto A, Lemos L et al (2003) Erdheim-Chester disease: a unique presentation with liver involvement and vertebral osteolytic lesions. Arch Pathol Lab Med 127:e337–e339
Lyders EM, Kaushik S, Perez-Berenguer J et al (2003) Aggressive and atypical manifestations of Erdheim-Chester disease. Clin Rheumatol 22:464–466
Waite RJ, Doherty PW, Liepman M et al (1988) Langerhans cell histiocytosis with the radiographic findings of Erdheim-Chester disease. Eur J Radiol 30:70–74
Klieger MR, Schultz E, Elkowitz DE et al (2002) Erdheim-Chester disease: a unique presentation with multiple osteolytic lesions of the spine and pelvis that spared the appendicular skeleton. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:429–432
Kambouchner M, Colby TV, Domenge C et al (1997) Erdheim-Chester disease with prominent pulmonary involvement associated with eosinophilic granuloma of mandibular bone. Histopathology 30:353–358
Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman RF (1990) sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol 7:19–73
Szekeres E, Tiba A, Korom I (1988) Xanthoma disseminatum: a rare condition with non-X, non lipid cutaneous histiocytopathy Dermatol Surg Oncol 14:1021–1024
Bohlega S, Alwatban J, Tulbah A et al (1997) Cerebral manifestation of Erdheim-Chester disease: clinical and radiologic findings. Neurology 49:1702–1705
Haroche J, Amoura Z, Dion E et al (2004) Cardiovascular involvement, an overlooked feature of Erdheim-Chester disease. Medicine 83:371–392
Vaglio A, Palmisano A, Corradi D et al (2007) Retroperitoneal fibrosis: evolving concepts. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 33:803–817
Remi-Jardin M, Remy J, Gosselin B et al (1993) Pulmonary involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: high resolution CT findings. Eur Radiol 3:389–392
Wittenberg KH, Swensen SJ, Myers JL (2000) Pulmonary involvement with Erdheim-Chester disease: radiographic and CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:1327–1331
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Filippo, M., Ingegnoli, A., Carloni, A. et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: clinical and radiological findings. Radiol med 114, 1319–1329 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-009-0473-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-009-0473-8