Abstract
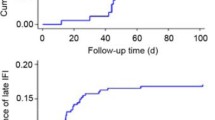
Invasive filamentous fungal infection (IFFI) is an important cause of mortality in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients. We reviewed 22 consecutive cases of IFFI in allogeneic HSCT recipients at Roswell Park Cancer Institute. IFFI was diagnosed after neutrophil recovery in 21 patients (95%). All had received corticosteroids within 1 month prior to IFFI diagnosis. Fourteen (64%) presented with dyspnea, and only 7 (32%) were febrile. Aspergillus species were isolated in 18 (82%) cases. Thirty day mortality after IFFI diagnosis was associated with a higher mean daily dose of corticosteroids (P = 0.02) and receiving OKT3 (P = 0.01) within 1 month prior to IFFI diagnosis and serum creatinine >2 mg/dl at the time of diagnosis (P = 0.004). Histopathologic material from biopsy or autopsy was available in 15 patients (68%). In 8 (53%), the predominant lung histopathology was an acellular coagulative necrosis and hyphal angioinvasion was observed in some of these cases. These findings have generally been observed in neutropenic patients but not in non-neutropenic HSCT recipients. The predominance of coagulative necrosis in our series may reflect the high doses of corticosteroids used to treat graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), which may have disabled leukocyte trafficking and hyphal killing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SL Gerson GH Talbot S Hurwitz BL Strom EJ Lusk PA. Cassileth (1984) ArticleTitleProlonged granulocytopenia: The major risk factor for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia Ann Intern Med 100 345–351
S Ascioglu JH Rex B Pauw Particlede et al. (2002) ArticleTitleDefining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: An international consensus Clin Infect Dis 34 7–14 Occurrence Handle10.1086/323335 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnosVOltg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11731939
J Berenguer MC Allende JW Lee et al. (1995) ArticleTitlePathogenesis of pulmonary aspergillosis. Granulocytopenia versus cyclosporine and methylprednisolone-induced immunosuppression Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 152 1079–1086
D Caillot O Casasnovas A Bernard et al. (1997) ArticleTitleImproved management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients using early thoracic computed tomographic scan and surgery J Clin Oncol 15 139–147
J Maertens J Van Eldere J Verhaegen E Verbeken J Verschakelen M Boogaerts (2002) ArticleTitleUse of circulating galactomannan screening for early diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients J Infect Dis 186 1297–1306 Occurrence Handle10.1086/343804 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovFKjtbw%3D Occurrence Handle12402199
J Maertens J Verhaegen K Lagrou J Van Eldere M Boogaerts (2001) ArticleTitleScreening for circulating galactomannan as a noninvasive diagnostic tool for invasive aspergillosis in prolonged neutropenic patients and stem cell transplantation recipients: A prospective validation Blood 97 1604–1610 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood.V97.6.1604 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitFalt70%3D Occurrence Handle11238098
Odabasi Z, Mattiuzzi G, Estey E et al. Beta-D-glucan as a diagnostic adjunct for invasive fungal infections: Validation, cutoff development, and performance in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 199–205. Epub 2004 Jun 28.
AS Pham JJ Tarrand GS May MS Lee DP Kontoyiannis XY Han (2003) ArticleTitleDiagnosis of invasive mold infection by real-time quantitative PCR Am J Clin Pathol 119 38–44
A Wald W Leisenring JA Burik Particlevan RA Bowden (1997) ArticleTitleEpidemiology of Aspergillus infections in a large cohort of patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation [see comments] J Infect Dis 175 1459–1466
JW Baddley TP Stroud D Salzman PG Pappas (2001) ArticleTitleInvasive mold infections in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients Clin Infect Dis 32 1319–1324
WB Grow JS Moreb D Roque et al. (2002) ArticleTitleLate onset of invasive aspergillus infection in bone marrow transplant patients at a university hospital Bone Marrow Transplant 29 15–19
E Jantunen P Ruutu L Niskanen et al. (1997) ArticleTitleIncidence and risk factors for invasive fungal infections in allogeneic BMT recipients Bone Marrow Transplant 19 801–808
PH McWhinney CC Kibbler MD Hamon et al. (1993) ArticleTitleProgress in the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis in bone marrow transplantation: 13Years experience Clin Infect Dis 17 397–404
KY Yuen PC Woo MS Ip et al. (1997) ArticleTitleStage-specific manifestation of mold infections in bone marrow transplant recipients: Risk factors and clinical significance of positive concentrated smears Clin Infect Dis 25 37–42
KA Marr RA Carter M Boeckh P Martin L Corey (2002) ArticleTitleInvasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: Changes in epidemiology and risk factors Blood 100 4358–4366
T Fukuda M Boeckh RA Carter et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRisks and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants after nonmyeloablative conditioning Blood 102 827–833
TF Patterson WR Kirkpatrick M White et al. (2000) ArticleTitleInvasive aspergillosis. Disease spectrum, treatment practices, and outcomes. I3 Aspergillus Study Group Medicine (Baltimore) 79 250–260
DW Denning (1996) ArticleTitleTherapeutic outcome in invasive aspergillosis Clin Infect Dis 23 608–615
JR Wingard P Kubilis L Lee et al. (1999) ArticleTitleClinical Significance of Nephrotoxicity in Patients Treated with Amphotericin B for Suspected or Proven Aspergillosis Clin Infect Dis 29 1402–1407
R Herbrecht DW Denning TF Patterson et al. (2002) ArticleTitleVoriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis New Engl J Med 347 408–415
DA Stevens (1998) ArticleTitleCombination immunotherapy and antifungal chemotherapy Clin Infect Dis 26 1266–1269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaukat, A., Bakri, F., Young, P. et al. Invasive filamentous fungal infections in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients after recovery from neutropenia: Clinical, radiologic, and pathologic characteristics. Mycopathologia 159, 181–188 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-004-5495-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-004-5495-0